Seismic Refraction Exploration for Groundwater Potential Evaluations: A Case Study of Vientiane Province, Laos
Main Article Content
Abstract
Recently, there h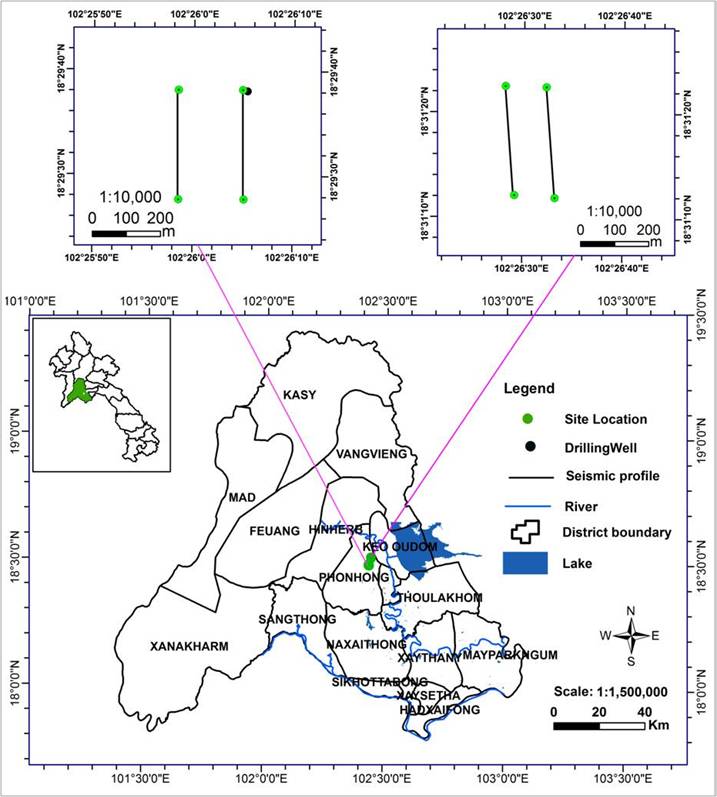
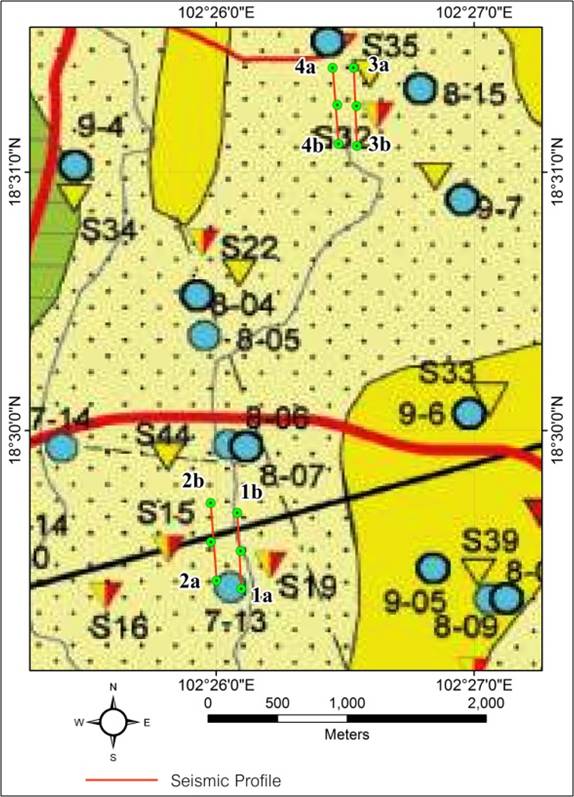
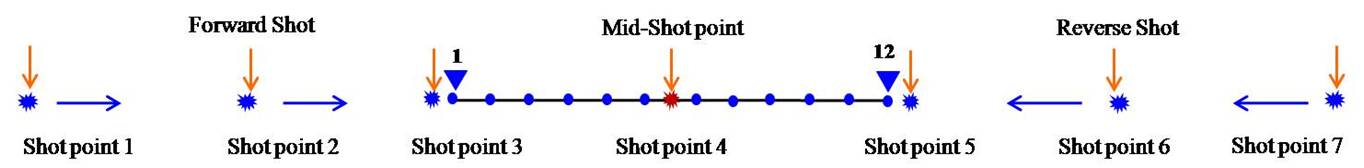
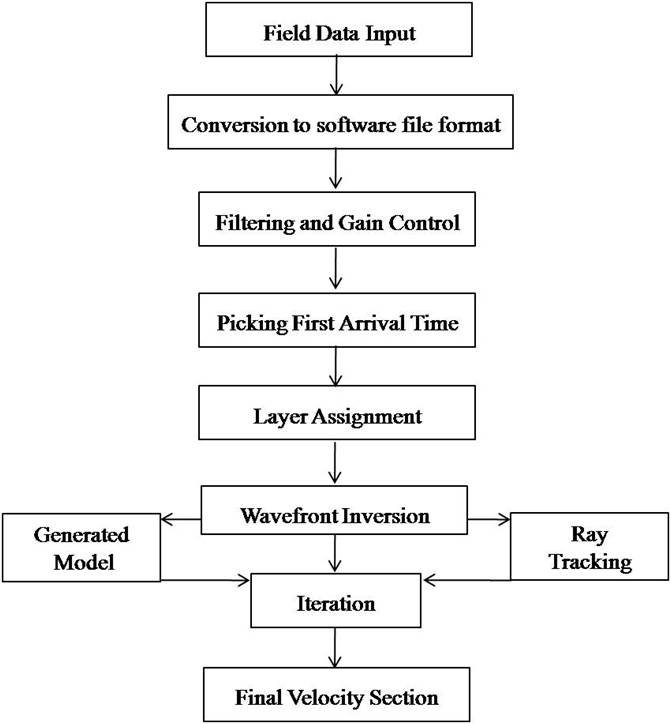
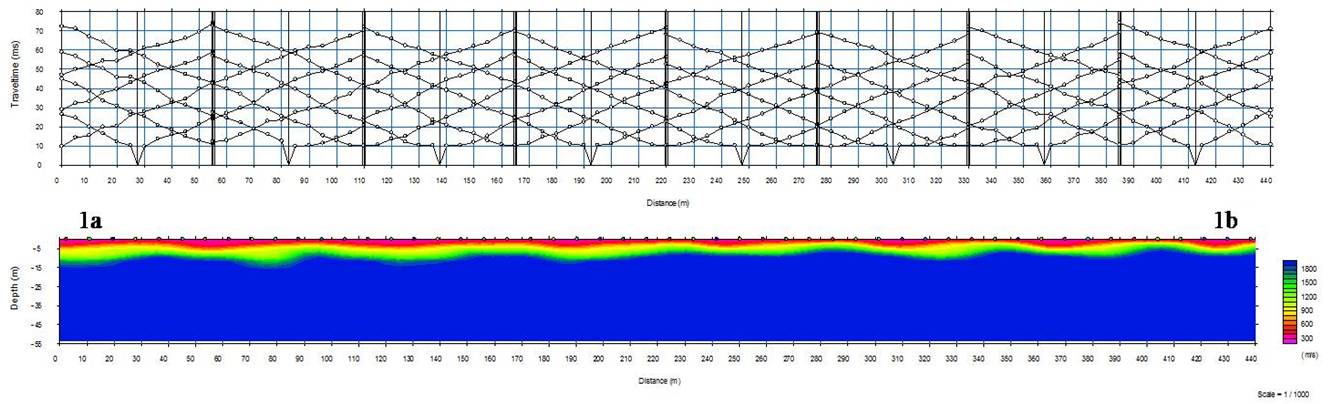
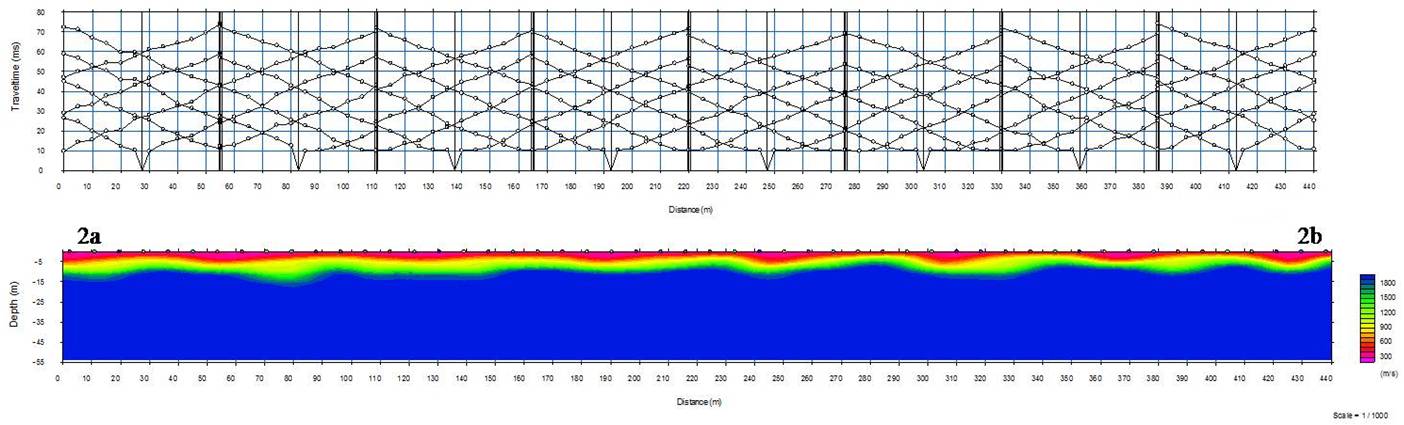
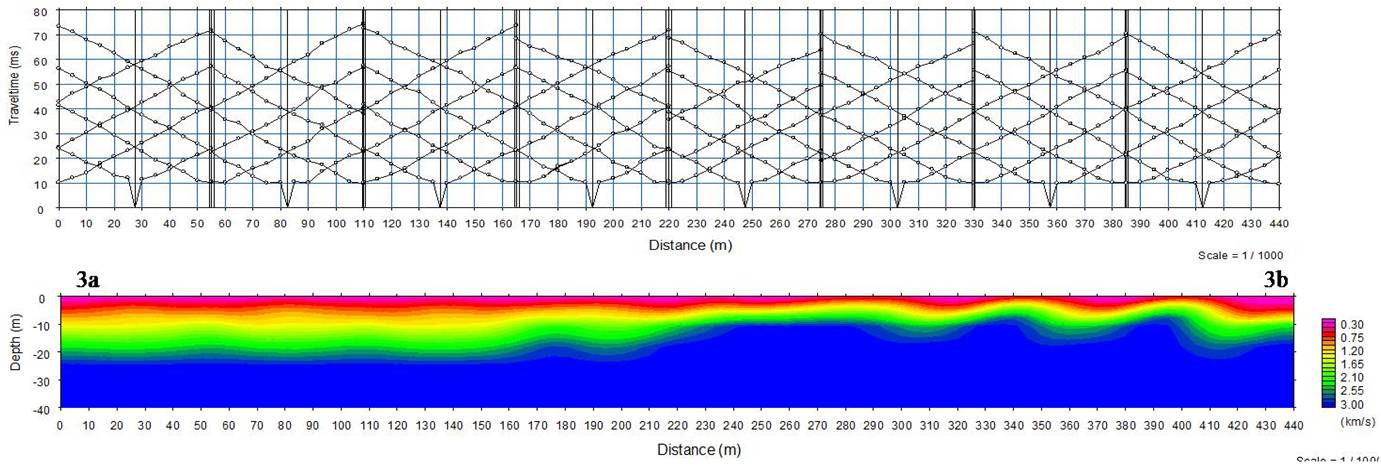
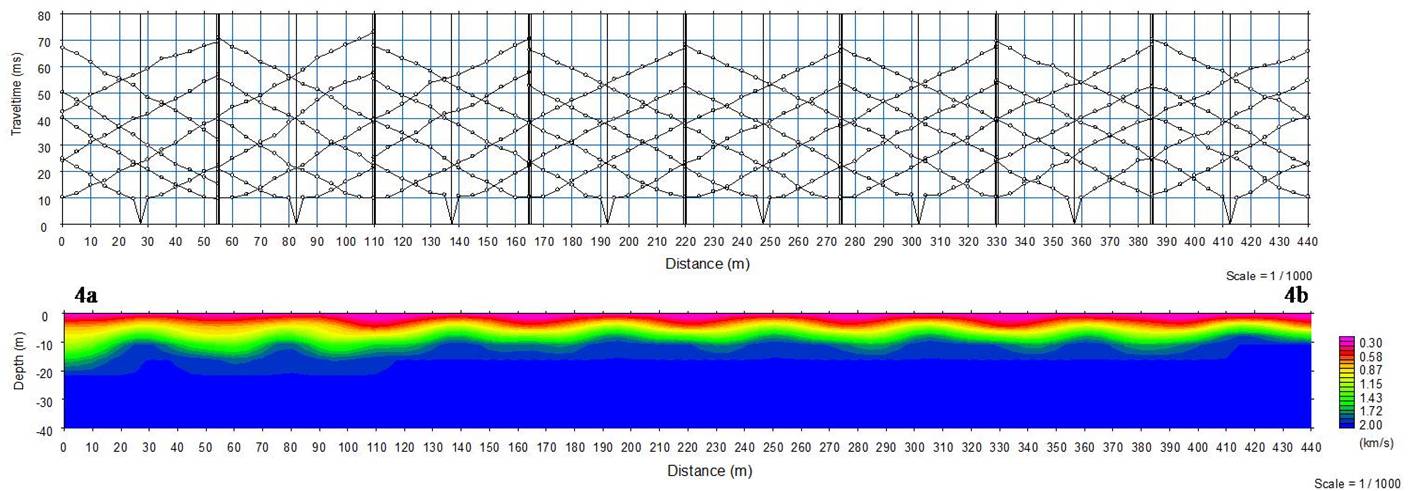
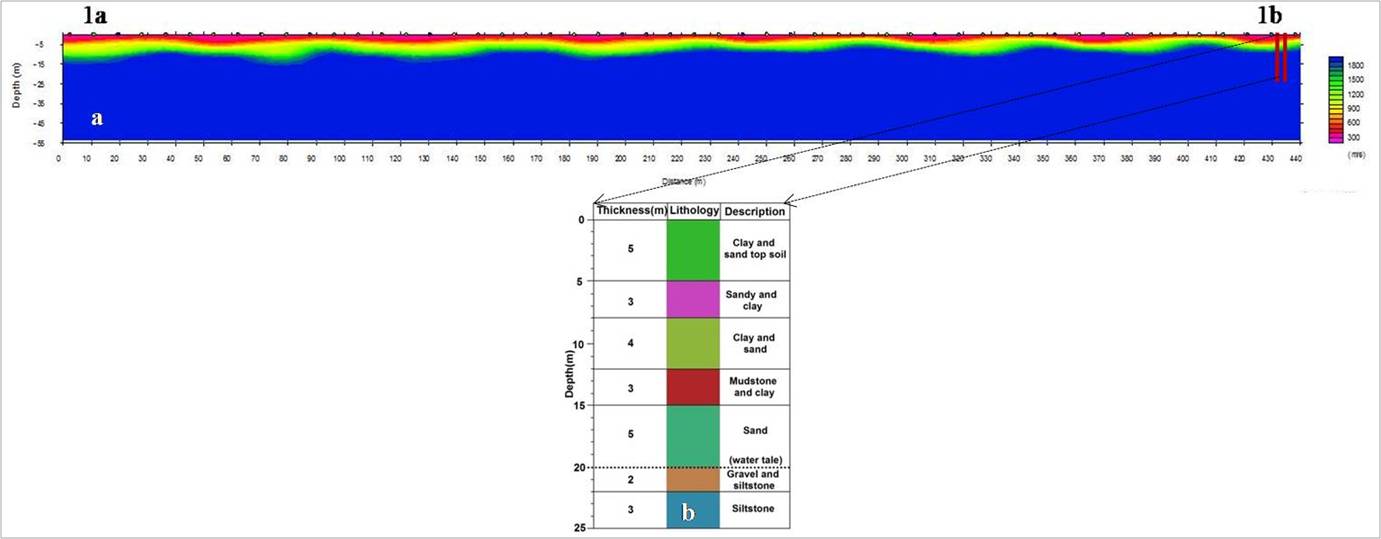 h vertical depth. This velocity in can delineate groundw
h vertical depth. This velocity in can delineate groundw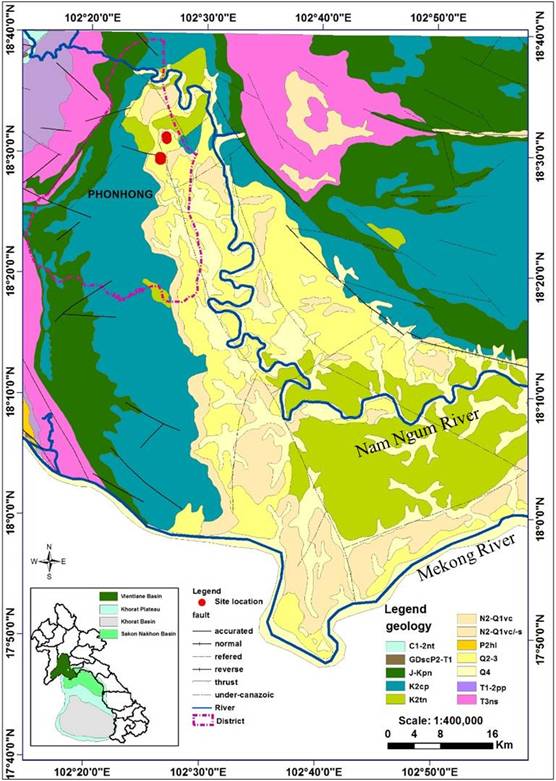
References
[1] M. Masaharu. Final Report for Economic Geology, the World Bank Washington DC (2006).
[2] H. Kyoochul, M.N. Nguyen Thi, L. Eunhee, J. Ramasamy. Current Status and Issues of Groundwater in the Mekong River Basin, Korea Institute of Geoscience and Mineral Resources (KIGAM) (2017), pp.1-125.
[3] Japan International Cooperation Agency (JICA). The study on rural water supply and sanitation improvement in the northwest region in the Lao People´s Democratic Republic, Ministry of health, National centre for environmental health and water supply, Progress report 2 (2000), pp.14.
[4] K. Takayanagi. Basic Design Study Report on the Project for Groundwater Development in Vientiane Province in Laos PDR. Japan International Cooperation Agency (JICA) (1993).
[5] C. Chiemeke, and Aboh. Delineation of aquiferous layers within the basement complex using joint inversion of seismic refraction tomography and high resolution 3D seismic reflection survey, Arch. Applied Sci. Res (2012), Vol. 4, pp. 400-405.
[6] M. El Tabakh, C. Utha-Aroon, B.C. Schreiber. Sedimentology of the Cretaceous Maha Sarakham evaporites in the Khorat Plateau of northeastern Thailand, Sedimentary Geology, Vol.123 (1999), pp.31-62.
[7] R.J. Hite, W. Japakasert. Potash deposits of the Khorat Plateau, Thailand and Laos, Economic Geology, Vol. 74 (1979), pp. 448-458.
[8] S. Keith, P. Crosby. Overview of the Geology and Resources of the APPC Udon Potash (Sylvinite) Deposits, Udon Thani Province, Thailand. International Conference on Geology, Geotechnology and Mineral Resources of Indochina (GEOINDO 2005), Khon Kaen, Thailand (2005), pp.283-299.
[9] F. L.S. Paul, B.S. Robert, B. Charlie, C. Andrew. Mid-Cretaceous inversion in the Northern Khorat Plateau of Lao PDR and Thailand, Tectonic Evolution of Southeast Asia, Vol. 106 (2016), pp. 233-247.
[10] Z. Xiying, M. Haizhou, M. Yunqi, T. Qiliang, Y. Xiaolong. Origin of the late Cretaceous potash-bearing evaporites in the Vientiane Basin of Laos, Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, Vol. 62 (2013), pp. 812–818.
[11] K. Phommakaysone. Urban geology of Vientiane municipality, capital of the Lao people’s Democratic Republic, Atlas of Urban Geology, Vol.14 (2001), pp.341-346.
[12] Raksaskulwong, M., and Monjai, D. Relationship between the Maha Sarakham Formation and high terrace gravels along the Khon Kean-Kalasin provinces. (Geothai’07), Department of Mineral Resources, Bangkok, Thailand (2007), pp.288-296.
[13] N.X. Long, N.X. Lam, N.D. Canh. Report on Geological data for Potassium and Manganese in Thangon. Department of Geology and Mining, Vientiane, Laos (1986).
[14] M. El Tabakh, C. Utha-Aroon, B.C. Schreiber. Sedimentology of the Cretaceous Maha Sarakham evaporites in the Khorat Plateau of northeastern Thailand, Sedimentary Geology, Vol.123 (1999), pp.31-62.
[15] M. Stuart-Fox, D.F. Rooney. Microsoft Encarta, (2006).
[16] P. Kearey, M. Brooks, I. Healy. An Introduction to Geophysical Exploration. 3rd ed. Blackwell Science (2002).
[17] G. Grelle, F.M. Guadagno. Seismic refraction methodology for groundwater level determination: “Water seismic index”. Journal of Applied Geophysics, Vol.68, (2009) pp. 301–320.
[18] B. Hasselstroem. Water prospecting and rock-investigation by the seismic refraction method. Geoexploration 7 (2) (1969), 213.
[19] S.A. Adedibu, C.O. Abimbola. Insight into seismic refraction and electrical resistivity tomography techniques in subsurface investigations, The Mining-Geology-Petroleum Engineering Bulletin, (2019), pp. 93-111.
[20] P. Nils, W. Kamhaeng, P. Khamphouth, E. Sten-Ake. Characterization of aquifers in the Vientiane Basin, Laos, using Magnetic Resonance Sounding and Vertical Electrical Sounding. Journal of Applied Geophysics 73, (2011a), pp. 207–220.
[21] P. Nils, W. Kamhaeng, P. Khamphouth, E. Sten-Ake. Determining water quality parameters of aquifers in the Vientiane Basin, Laos, using geophysical and water chemistry data. Near Surface Geophysics, Vol. 9, (2011b), pp. 381–395.
[2] H. Kyoochul, M.N. Nguyen Thi, L. Eunhee, J. Ramasamy. Current Status and Issues of Groundwater in the Mekong River Basin, Korea Institute of Geoscience and Mineral Resources (KIGAM) (2017), pp.1-125.
[3] Japan International Cooperation Agency (JICA). The study on rural water supply and sanitation improvement in the northwest region in the Lao People´s Democratic Republic, Ministry of health, National centre for environmental health and water supply, Progress report 2 (2000), pp.14.
[4] K. Takayanagi. Basic Design Study Report on the Project for Groundwater Development in Vientiane Province in Laos PDR. Japan International Cooperation Agency (JICA) (1993).
[5] C. Chiemeke, and Aboh. Delineation of aquiferous layers within the basement complex using joint inversion of seismic refraction tomography and high resolution 3D seismic reflection survey, Arch. Applied Sci. Res (2012), Vol. 4, pp. 400-405.
[6] M. El Tabakh, C. Utha-Aroon, B.C. Schreiber. Sedimentology of the Cretaceous Maha Sarakham evaporites in the Khorat Plateau of northeastern Thailand, Sedimentary Geology, Vol.123 (1999), pp.31-62.
[7] R.J. Hite, W. Japakasert. Potash deposits of the Khorat Plateau, Thailand and Laos, Economic Geology, Vol. 74 (1979), pp. 448-458.
[8] S. Keith, P. Crosby. Overview of the Geology and Resources of the APPC Udon Potash (Sylvinite) Deposits, Udon Thani Province, Thailand. International Conference on Geology, Geotechnology and Mineral Resources of Indochina (GEOINDO 2005), Khon Kaen, Thailand (2005), pp.283-299.
[9] F. L.S. Paul, B.S. Robert, B. Charlie, C. Andrew. Mid-Cretaceous inversion in the Northern Khorat Plateau of Lao PDR and Thailand, Tectonic Evolution of Southeast Asia, Vol. 106 (2016), pp. 233-247.
[10] Z. Xiying, M. Haizhou, M. Yunqi, T. Qiliang, Y. Xiaolong. Origin of the late Cretaceous potash-bearing evaporites in the Vientiane Basin of Laos, Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, Vol. 62 (2013), pp. 812–818.
[11] K. Phommakaysone. Urban geology of Vientiane municipality, capital of the Lao people’s Democratic Republic, Atlas of Urban Geology, Vol.14 (2001), pp.341-346.
[12] Raksaskulwong, M., and Monjai, D. Relationship between the Maha Sarakham Formation and high terrace gravels along the Khon Kean-Kalasin provinces. (Geothai’07), Department of Mineral Resources, Bangkok, Thailand (2007), pp.288-296.
[13] N.X. Long, N.X. Lam, N.D. Canh. Report on Geological data for Potassium and Manganese in Thangon. Department of Geology and Mining, Vientiane, Laos (1986).
[14] M. El Tabakh, C. Utha-Aroon, B.C. Schreiber. Sedimentology of the Cretaceous Maha Sarakham evaporites in the Khorat Plateau of northeastern Thailand, Sedimentary Geology, Vol.123 (1999), pp.31-62.
[15] M. Stuart-Fox, D.F. Rooney. Microsoft Encarta, (2006).
[16] P. Kearey, M. Brooks, I. Healy. An Introduction to Geophysical Exploration. 3rd ed. Blackwell Science (2002).
[17] G. Grelle, F.M. Guadagno. Seismic refraction methodology for groundwater level determination: “Water seismic index”. Journal of Applied Geophysics, Vol.68, (2009) pp. 301–320.
[18] B. Hasselstroem. Water prospecting and rock-investigation by the seismic refraction method. Geoexploration 7 (2) (1969), 213.
[19] S.A. Adedibu, C.O. Abimbola. Insight into seismic refraction and electrical resistivity tomography techniques in subsurface investigations, The Mining-Geology-Petroleum Engineering Bulletin, (2019), pp. 93-111.
[20] P. Nils, W. Kamhaeng, P. Khamphouth, E. Sten-Ake. Characterization of aquifers in the Vientiane Basin, Laos, using Magnetic Resonance Sounding and Vertical Electrical Sounding. Journal of Applied Geophysics 73, (2011a), pp. 207–220.
[21] P. Nils, W. Kamhaeng, P. Khamphouth, E. Sten-Ake. Determining water quality parameters of aquifers in the Vientiane Basin, Laos, using geophysical and water chemistry data. Near Surface Geophysics, Vol. 9, (2011b), pp. 381–395.
